A kidney stone is a solid, pebble-like piece of material that can form in one or both of your kidneys when high levels of certain minerals are in your urine. Kidney stones rarely cause permanent damage if treated by a health care professional.
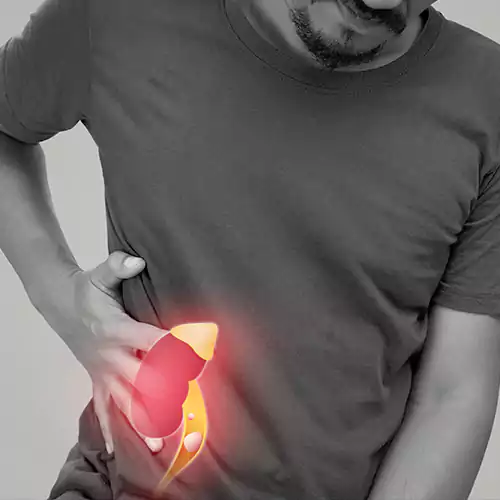
You may have a kidney stone if you feel a sharp pain in your back, side, lower abdomen, or groin; or have blood in your urine. If you have a small stone that easily passes through your urinary tract, you may not have symptoms at all.
Health care professionals use your medical history, a physical exam, and tests to diagnose kidney stones. The tests may also be able to show problems that caused a kidney stone to form.
Health care professionals may treat your kidney stones by removing the kidney stone or breaking it into small pieces. You may be able to prevent kidney stones by drinking enough water, changing the way you eat, or taking medicines.
If you have kidney stones, drink lots of water unless otherwise directed by a health care professional. You may be able to prevent future kidney stones by making changes in how much sodium, animal protein, calcium, and oxalate you consume.