The main function of dialysis will be to “clean” the blood of the toxins generated, excess water and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, which is caused by a defect in its elimination by the kidney. Dialysis is applied in patients with acute renal failure (reversible) and mainly in those patients with chronic renal failure in the terminal phase and incompatible with life.
It is based on the movement of solutes (ions, urea, creatinine, uric acid, etc.) and solvents (water) through the pores of a semipermeable membrane in relation to the different concentrations of substances following diffusion phenomena, Osmosis, and filtration.
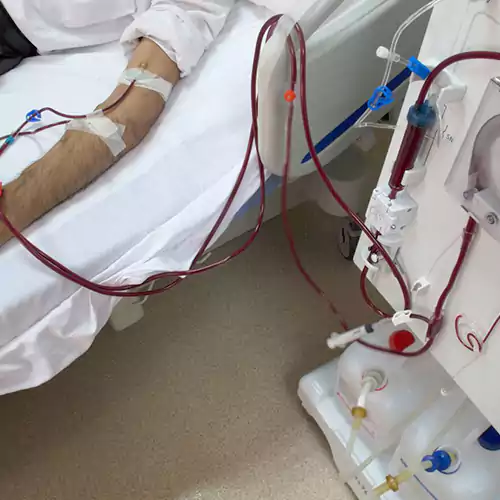
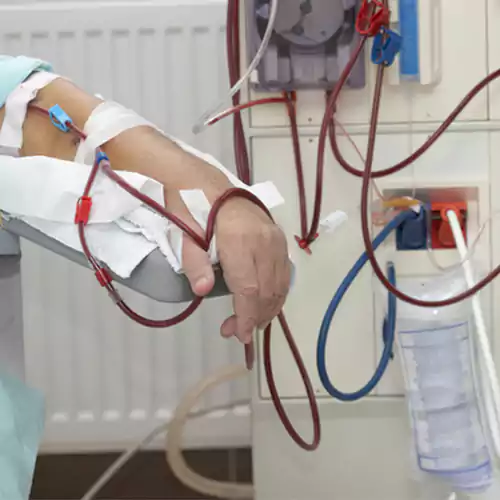
The fundamental indication of dialysis is the treatment of chronic renal failure, which should always be comprehensive, this is with options for changing from one technique to another and the possibility of kidney transplant in case there is no contraindication. The diseases that lead to renal failure are multiple, but the main ones are glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, interstitial nephritis, vascular nephropathies, and diabetic nephropathy. Dialysis is also indicated in acute renal failure and in some poisonings
When the semipermeable membrane is artificial. These can be cellulosic or synthetic in nature and because of their structure they can be capillary fiber or flat membrane. They vary by their permeability, surface, thickness, electric charge and adsorption capacity.
A permanent access route to the intravascular torrent is required (preferably an internal arteriovenous fistula, possible a cannula, etc.), an artificial kidney (consisting of a blood pump, a monitor and the dialyzer where the semipermeable membrane is located and where the exchange between the fluid or dialysis bath and the blood takes place). Usually, the dialysis session in chronic patients takes place three days a week (Monday, Wednesday and Friday; or Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday), with a duration of 4 hours per session, in morning, afternoon or evening shifts. It can be carried out in the hospital, in an outpatient dialysis unit or even at the patient’s own home.
The main complications are insufficient blood flow (the ideal is greater than 300 cm./min.), Dialysate rupture with blood loss, hypotension, dizziness, headache, nausea or vomiting, itching, cramping, etc. Currently, with modern automatic machines and various variants of bicarbonate dialysis, complications are minimal and largely rectifiable.
When the semipermeable membrane is natural, as in the case of the patient’s peritoneum (a layer that covers the internal organs of the abdomen and that has multiple capillaries and large surface area).
Peritoneal dialysis requires the placement of a soft multi-perforated catheter in the abdomen, through which dialysis solution (similar to the liquid part of the blood but without waste products) is infused, about two liters with replacement every 4-6 hours during the day and about 8 hours at night, every day of the year. This method of dialysis is called continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and is performed by the patient himself after a period of hospital learning. It can also be done with a machine or cycler that performs the spare parts on a scheduled basis at night, allowing the patient to be free throughout the day and this is called automated peritoneal dialysis. When the kidneys are healthy, they cleanse their blood. They also produce hormones that keep your bones strong and your blood healthy. When the kidneys fail, treatment is needed to replace the work they performed. Unless you receive a kidney transplant, you will need a treatment called dialysis. Dialysis is the technique that partially replaces the function of the kidneys, such as the depurative and normalizing function of the fluid and the composition of the blood. To do this, a membrane is used that contacts the blood, which acts as a filter through which blood filtration occurs imitating what the kidneys would do. The functions of formation of Erythropoietin and production of active Vitamin D do not carry them out and therefore this treatment must be added.
There are two types of dialysis, peritoneal dialysis, and hemodialysis.
The Peritoneal Dialysis is the one that is performed in the peritoneal cavity and uses as a filter the natural peritoneal membrane that surrounds the entire cavity. So that the purification of the blood can be carried out, a special liquid (dialysis fluid) that is periodically replaced is introduced through a soft silicone tube into the peritoneal cavity. It is a simple technique that is performed at home (it is a home dialysis option). The Hemodialysis, it is the one that uses the blood of the patient, making it pass through an artificial filter on the outside and it is at the level of this filter where the depurative and normalizing function of the liquid and composition of the blood is performed. It is a technique that is performed primarily in hospital units or in dialysis center in Delhi, although home hemodialysis treatment is currently also being developed.
Broadly speaking, we could say that both techniques are superimposable in their function of partially replacing renal function. Peritoneal dialysis is performed at home and it is the patient himself who performs after a short period of guidance by
dialysis specialist, is continuous throughout the day and therefore more physiological and above all, allows the patient to perform their freedom more freely. usual social and work activity. Hemodialysis
is usually performed in hospital units or dialysis center in Nashik usually 3 times a week (in some it is daily and shorter) every other day and at fixed pre-established times, this often prevents reconciliation
with the labor and social activity, in addition to the fact that being an intermittent technique makes it less physiological by more abrupt changes. Nowadays, home hemodialysis programs are being developed that overcome
these problems.